Exercise Daily – Building balanced meals is essential for maintaining a healthy diet and promoting long-term well-being in today’s fast-paced world. A well-balanced meal plan ensures you eat various foods that provide the vital nutrients your body needs. Focus on meals that include a combination of macronutrients, complex carbohydrates for stable energy, lean protein for muscle repair, and healthy fats to support heart health and the body’s ability to absorb fat-soluble vitamins.
For example, meals with whole grains, vegetables, and fruits and sources of lean protein like poultry or legumes can help increase your nutrient intake while keeping you full after a meal. Adding healthy fat sources, such as olive oil, avocados, or nuts, can further enhance feelings of fullness and support your overall health. When creating a meal plan for athletes or active individuals, aim to include foods like whole grains, vegetables, fruits, and lean proteins to support energy needs and muscle recovery.
Healthy fats like olive oil and avocados help control long-term energy and inflammation. Exercise Daily guidelines recommend filling half your plate with vegetables and fruits, ensuring your weekly meals provide a wide range of nutrients. Whether grocery shopping or prepping meals, choose lean cuts of meat and plant-based proteins to lower the risk of developing heart disease. If you’re unsure how to meet your nutritional needs, consider consulting a registered dietitian for personalized nutrition tips that align with your body weight and physical activity levels.

What is a Balanced Meal?
A balanced meal is one that provides your body with all the essential nutrients it needs to function at its best. It’s not just about hitting a certain calorie number; it’s about making every bite count. Think of a balanced meal as a symphony of nutrients, where each food group plays a unique and crucial role. They help your body maintain energy, repair tissues, and support immune function.
A balanced meal typically includes a variety of macronutrients such as carbohydrates, proteins, and fats, as well as micronutrients like vitamins and minerals. Incorporating diverse food groups ensures your body gets the nutrients required for optimal functioning.
The Importance of a Balanced Meal
Balanced meals are essential for numerous reasons. First and foremost, they help maintain a healthy weight by providing the right amount of energy for your body’s needs. Moreover, balanced meals improve your energy levels, help reduce cravings for unhealthy snacks, and reduce the risk of chronic diseases like heart disease, type 2 diabetes, and certain types of cancer. By providing various nutrients, balanced meals support brain function, heart health, and digestive wellness.
Athletes should also consider the timing of meals and snacks. Eating a balanced meal containing carbs, protein, and fat 3-4 hours before training can fuel workouts. After exercise, consuming carbs and protein within 30 minutes to an hour helps replenish glycogen stores and repair muscles. Hydration is also critical; water and electrolytes need to be consistently replenished. Tailoring the meal plan to the specific demands of the sport, training intensity, and individual dietary needs can optimize athletic performance and recovery.
Key Components of a Balanced Meal
Creating a balanced meal involves selecting the right ingredients from different food groups. This ensures that you receive all the nutrients needed for overall health. Let’s break down the key components of a balanced meal and explore how they contribute to your well-being.
1. Fruits and Vegetables
Aim to fill half of your plate with fruits and vegetables. These are rich in vitamins, minerals, antioxidants, and fiber, all of which are vital for good health. The fiber in fruits and vegetables helps maintain healthy digestion and keeps you feeling full, while the antioxidants help protect your cells from damage. Various colors in your produce selection are also important because different colors often indicate different nutrients.
Examples:
- Dark leafy greens like spinach and kale for iron and calcium
- Bright orange and yellow fruits like carrots and mangoes for vitamin A
- Berries for antioxidants
2. Protein Sources
Protein is a fundamental part of a balanced meal because it supports muscle repair, immune function, and overall cell growth. Include lean protein sources, such as chicken, fish, eggs, legumes, or plant-based proteins like tofu and tempeh. Plant-based proteins like beans, lentils, quinoa, and nuts are excellent choices for vegetarians or vegans.
Examples:
- Grilled chicken or turkey breast
- Salmon or other fatty fish for omega-3s
- Lentils or beans for plant-based protein
3. Whole Grains
Whole grains are a great source of carbohydrates, which your body uses for energy. Unlike refined grains, whole grains retain all parts of the grain, including the bran, germ, and endosperm, which are rich in fiber, B vitamins, and other nutrients. Choose whole grains like brown rice, quinoa, oats, or whole wheat bread to ensure you’re consuming slow-digesting carbs that keep you full longer.
Examples:
- Brown rice or quinoa as a base for meals
- Whole wheat bread for sandwiches
- Oatmeal for breakfast
4. Healthy Fats
Healthy fats are often misunderstood but essential for heart, brain, and cell health. They also help your body absorb fat-soluble vitamins (A, D, E, and K). Include sources of unsaturated fats in your diet, such as avocados, olive oil, nuts, and seeds. These fats can help reduce bad cholesterol levels and support heart health.
Examples:
- A handful of almonds or walnuts for a snack
- Drizzling olive oil over salads
- Incorporating chia or flax seeds into smoothies or yogurt
5. Dairy and Alternatives
Dairy products like milk, yogurt, and cheese provide calcium and vitamin D, which are important for maintaining bone health. For those who are lactose intolerant or follow a vegan diet, alternatives like almond milk, soy milk, or fortified plant-based yogurts can also provide essential nutrients.
Examples:
- Low-fat yogurt with fruit for a snack
- Almond or soy milk in smoothies
- Cheese as a topping for soups or salads
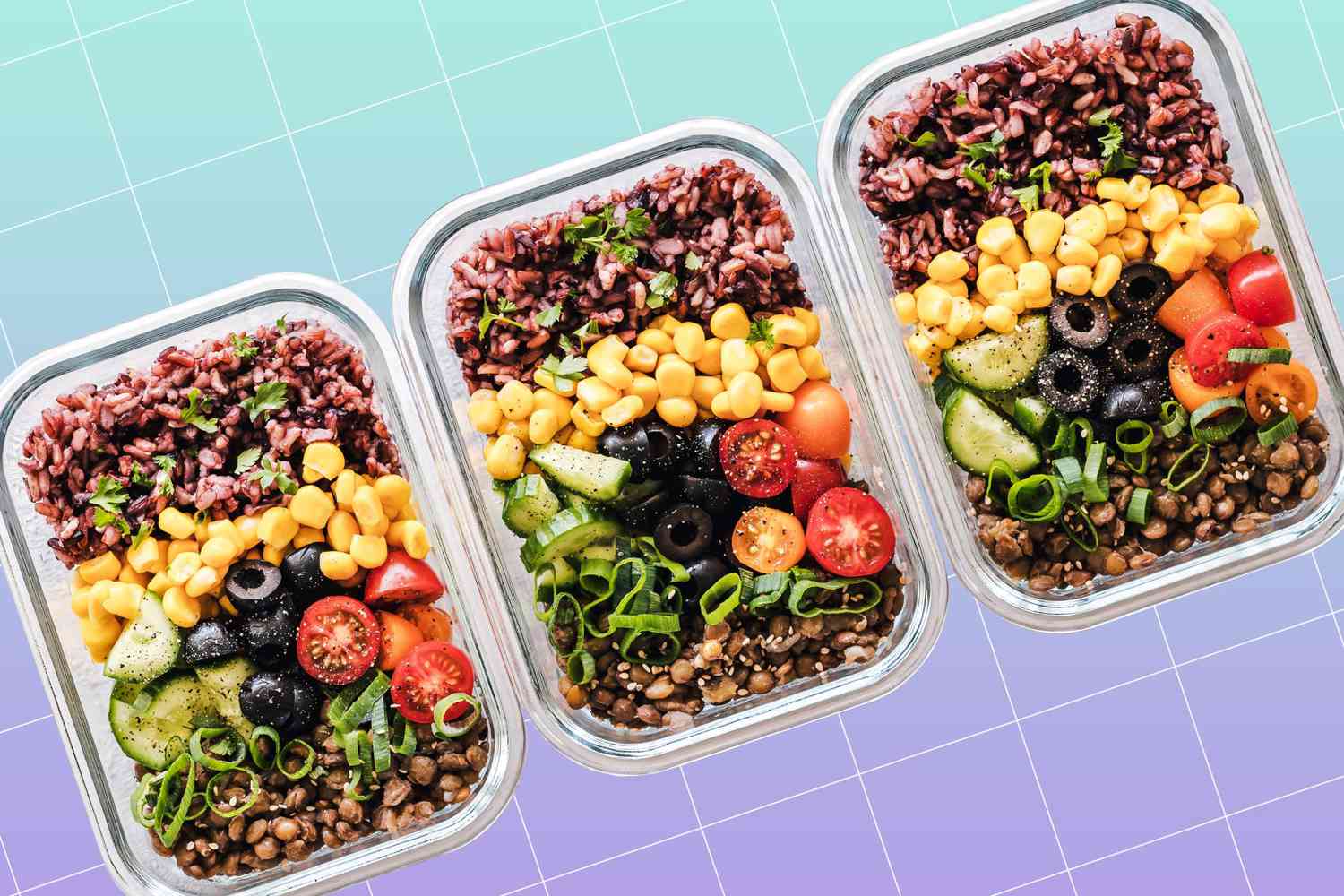

The Plate Method for Balanced Meals
The plate method is a simple and effective visual tool to create balanced meals without the need for counting calories. It involves dividing your plate into three key sections:
- Half for fruits and vegetables
- One-quarter for whole grains
- One-quarter of lean proteins
This visual guide ensures your meal is nutritionally balanced and helps you stay on track with portion sizes.
Benefits of the Plate Method
The plate method is flexible and adaptable to various diets and preferences. It allows you to see, at a glance, whether you’re including all the essential food groups and keeps portion sizes in check. This method eliminates the need for complicated tracking apps or calculators, making following a healthy eating plan easier.
Portion Sizes: Getting it Right
Portion control is just as important as the types of food you’re eating. Even healthy foods can lead to weight gain if eaten in excess. Understanding portion sizes helps you avoid overeating while ensuring you’re consuming the right nutrients.
Why Portion Control Matters
Consuming too much food can lead to imbalances in your diet and excess calorie intake, contributing to weight gain and other health issues. Portion control allows you to manage your calorie intake without sacrificing the quality or variety of foods.
Practical Tips for Managing Portion Sizes
- Use smaller plates: Studies show that using smaller plates can help reduce portion sizes without making you feel deprived.
- Avoid eating straight from the package: Always portion out snacks to avoid eating more than intended.
- Listen to your body: Eat slowly and heed your body’s hunger and fullness cues.
- Meal prep: Planning and portioning meals in advance can help you avoid overeating.
Common Mistakes to Avoid When Creating a Meal Plan
While building a balanced meal plan is straightforward, a few common pitfalls can disrupt your nutritional balance. Avoiding these mistakes will keep you on the path to success.
1. Overloading on Carbs
Carbohydrates are essential for energy, but consuming too many refined carbs, like white bread and pasta, can throw off the balance of your meal. Opt for whole grains instead and ensure you’re getting plenty of protein and vegetables to round out your meals.
2. Forgetting Healthy Fats
In an effort to cut calories, some people avoid fats entirely. However, this can deprive your body of essential nutrients. Healthy fats are vital for hormone regulation, brain function, and heart health. Add small amounts of nuts, seeds, or oils to your meals to maintain a balanced diet.
How to Create a Weekly Balanced Meal Plan
Planning your meals ahead of time can help you stay organized, reduce stress, and ensure you’re consistently eating a well-balanced diet. Here’s how to create a weekly meal plan that works for you.
Planning Meals for Different Times of the Day
Each meal should contain a balance of protein, whole grains, and fruits or vegetables, whether it’s breakfast, lunch, or dinner. Snacks can also be part of a healthy eating plan, but ensure they include a balance of nutrients rather than empty calories.
Building Meals for a Healthy Weight
Focus on nutrient-dense, low-calorie foods that keep you full and satisfied without overeating. For example, a salad with lean protein and avocado balances fats, protein, and fiber without excessive calories.

Conclusion
Creating a balanced meal plan doesn’t have to be complicated. By focusing on including a variety of food groups in every meal, using tools like the plate method, and being mindful of portion sizes, you can easily develop a meal plan that supports your health and well-being. The key is consistency; making small, sustainable changes to your eating habits will help you achieve long-term success. Eating a balanced diet is a lifelong journey, so embrace the process and enjoy the benefits of nourishing your body properly.
FAQs – How to Create a Balanced Meal Plan
Q: What is the ideal plate ratio for a balanced meal?
A: The ideal plate ratio is half fruits and vegetables, one-quarter whole grains, and one-quarter protein.
Q: Can I still have snacks on a balanced meal plan?
A: Yes, your snacks balance nutrients like protein, healthy fats, and fiber.
Q: How can I incorporate more whole grains into my meals?
A: Swap refined grains for whole grains like brown rice, quinoa, or whole wheat bread.
Q: Do I need to count calories to create a balanced meal?
A: No, using the plate method and controlling portion sizes will help you create balanced meals without calorie counting.
Q: What are some easy sources of protein for vegetarians?
A: Vegetarian protein sources include lentils, beans, tofu, and quinoa, which offer various nutrients.