Exercise Daily – Swimming is a physically demanding sport that requires a combination of strength, endurance, and technique. While spending time in the water is essential for improving swimming skills, incorporating gym workouts into a swimmer’s training routine can provide significant benefits. We will explore various Gym Workouts for Swimmers that can enhance swimming performance, including weight training, competitive swimming workouts, agility exercises, and spin workouts. We will also delve into the health benefits of swimming.
Swimmers looking to improve their performance can benefit greatly from incorporating gym workouts into their training regimen. While swimming primarily works the muscles of the upper body, gym workouts allow swimmers to target specific muscle groups, build strength and endurance, improve flexibility, and enhance overall conditioning. By combining swimming with targeted gym exercises, swimmers can maximize their potential in the water.
Importance of Gym Workouts for Swimmers
Gym workouts play a crucial role in enhancing swimming performance by addressing specific areas that swimming alone may not fully target. These workouts help build overall strength, increase power, improve endurance, and work on essential stability and agility. Additionally, gym workouts can help prevent injuries by strengthening supporting muscles and correcting muscle imbalances.
Key Considerations for Gym Workouts
Before diving into the specific gym workouts, it’s important to understand a few key considerations to make the most out of your training sessions:
1. Understanding the Different Muscle Groups
Swimmers should have a good understanding of the different muscle groups involved in swimming. This knowledge will help them target specific areas for improvement and ensure a balanced training routine.
2. Balancing Strength and Flexibility
Swimmers need a balance between strength and flexibility. While strength allows for powerful strokes, flexibility enables a greater range of motion and proper technique. Finding the right balance is crucial to optimize swimming performance.
3. Incorporating Cardiovascular Exercises
In addition to strength and flexibility training, swimmers should include cardiovascular exercises to improve their overall fitness levels. This can be achieved through activities such as running, cycling, or using cardio equipment like ellipticals or rowing machines.
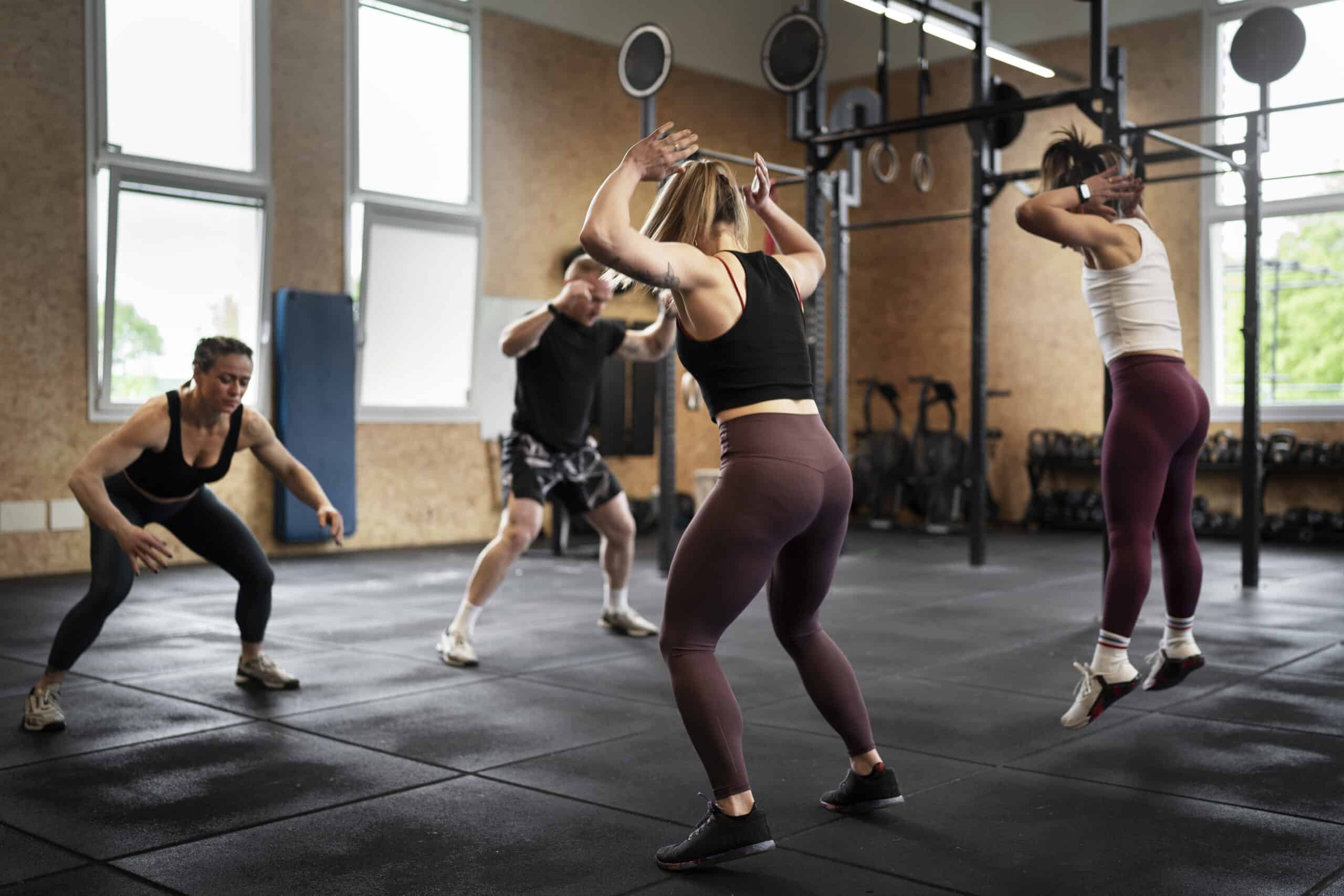
Weight Workouts for Swimmers
Weight training is an excellent way for swimmers to build strength and power. Here are some key weight workouts that can benefit swimmers:
1. Upper Body Strength: Chest and Arms
- Bench Press: This exercise targets the pectoral muscles and triceps, helping swimmers develop power during the pulling motion.
- Dumbbell Flys: By isolating the chest muscles, this exercise enhances upper body strength and helps maintain a strong and efficient swimming posture.
- Tricep Dips: Focusing on the triceps, this exercise aids in the propulsion phase of the swim stroke.
2. Core Stability: Abs and Lower Back
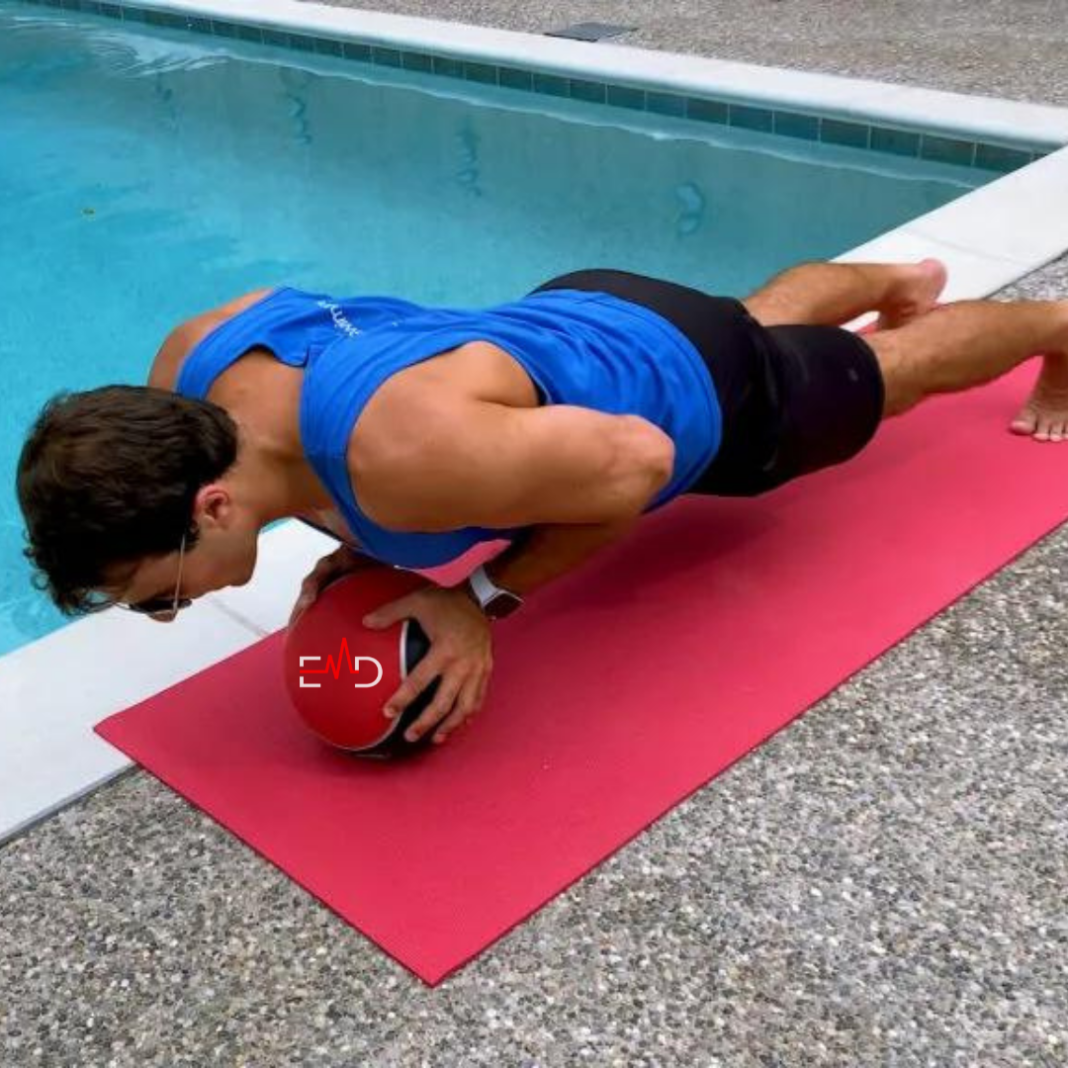
- Plank: A simple yet effective exercise, the plank helps strengthen the core muscles, which are crucial for maintaining stability and body control in the water.
- Russian Twists: This exercise engages the obliques and lower back, improving rotational strength and stability during swimming movements.
- Superman Pose: Targeting the lower back muscles, the superman pose helps build strength and endurance in the posterior chain.
3. Lower Body Strength: Legs and Glutes
- Squats: A compound exercise that engages multiple muscle groups, including the quadriceps, hamstrings, and glutes, squats are essential for leg strength.
- Lunges: Working on one leg at a time, lunges help build leg strength, stability, and balance.
- Calf Raises: Strengthening the calf muscles is important for generating powerful kicks during swimming.

Competitive Swimming Workouts for Swimmers
Competitive swimmers need to focus on specific training methods to improve their performance in races. Here are three key types of competitive swimming workouts:
1. Interval Training
Interval training involves alternating between periods of high-intensity swimming and recovery. This type of training improves cardiovascular fitness, builds endurance, and enhances speed.
2. Endurance Training
Endurance training involves long-distance swimming at a moderate intensity. It helps swimmers develop the stamina required to maintain consistent performance over extended periods.
3. Power Training
Power training focuses on explosive movements to build strength and speed. This type of training often includes drills that involve quick starts, turns, and sprints.
Agility Workouts for Swimmers
Agility workouts improve swimmers’ ability to change direction quickly, maintain balance, and execute precise movements in the water. Here are some effective agility exercises:
1. Lateral Movements
- Lateral Lunges: These lunges involve side-to-side movements, targeting the inner and outer thighs, as well as the glutes and quadriceps.
- Side Shuffle: Mimicking the lateral movements in swimming, side shuffles help improve quickness and lateral stability.
2. Quick Feet Drills
- Speed Ladder: Performing various footwork patterns in a speed ladder helps enhance foot speed and coordination.
- High Knees: This exercise involves running in place while lifting the knees as high as possible, improving overall leg speed and strength.
3. Plyometric Exercises
- Box Jumps: Plyometric exercises like box jumps enhance explosive power and leg strength, translating to more forceful starts and turns in the water.
- Depth Jumps: By jumping from a raised platform and immediately jumping vertically, swimmers develop reactive strength and explosive power.
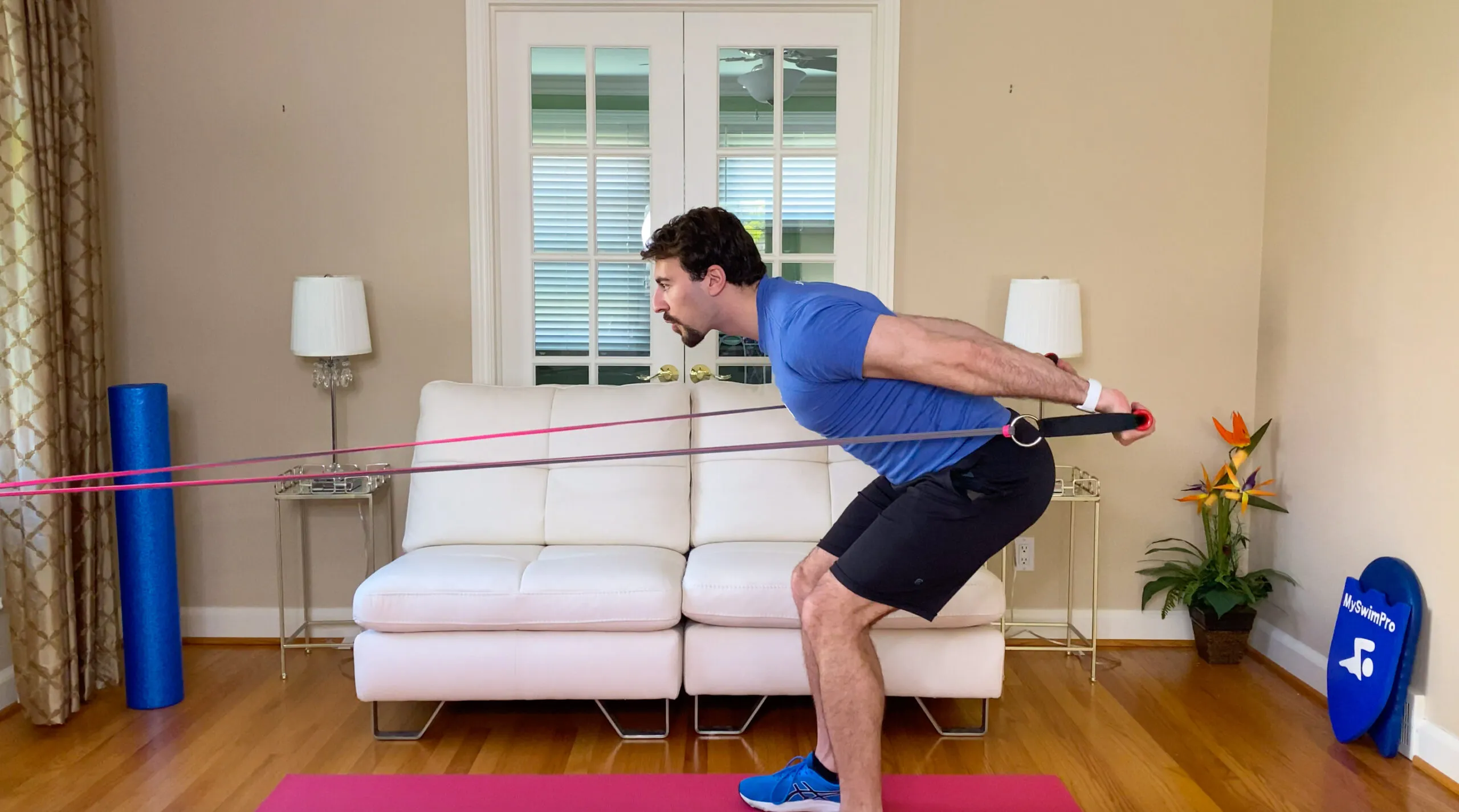

Spin Workouts for Swimmers
Spinning, a popular indoor cycling activity, can also benefit swimmers in several ways:
1. Benefits of Spinning
- Cardiovascular Endurance: Spin workouts provide an intense cardiovascular workout, improving heart and lung function.
- Leg Strength and Endurance: The resistance used during spinning helps build leg strength and endurance, crucial for powerful kicks in swimming.
2. Spinning Techniques for Swimmers
- Cadence Training: Focus on pedaling at various speeds, simulating different intensities of swimming strokes.
- Interval Training: Alternate between high-intensity sprints and recovery periods to mimic the demands of competitive swimming.
Benefits of Weight Workouts for Swimmers
- Increased Power: Weight training exercises such as squats, deadlifts, and lunges target major muscle groups and improve explosive power, translating into stronger starts, turns, and finishes in races.
- Improved Endurance: Weight workouts with high repetitions and low weights enhance muscular endurance, allowing swimmers to maintain technique and speed throughout long-distance races.
- Enhanced Stroke Efficiency: Strengthening the muscles involved in each swimming stroke helps swimmers maintain proper form and technique, resulting in more efficient and effective movements in the water.
- Injury Prevention: By strengthening weak areas and correcting muscle imbalances, weight workouts help prevent injuries commonly associated with swimming, such as shoulder impingement and lower back pain.
Health Benefits of Swimming
Beyond the specific gym workouts, swimming itself offers numerous health benefits, including:
1. Cardiovascular Fitness
Swimming is a fantastic aerobic exercise that strengthens the heart and improves overall cardiovascular health.
2. Muscle Strength and Endurance
Swimming engages all major muscle groups, helping to build strength and endurance throughout the body.
3. Improved Flexibility
The range of motion required for swimming promotes flexibility and joint mobility.
4. Stress Relief
Swimming is a low-impact exercise that can help reduce stress and promote relaxation.
5. Low Impact on Joints
The buoyancy of water reduces stress on the joints, making swimming a suitable exercise for people with joint conditions or injuries.

Physical Health Benefits
1. Full-body workout
Swimming engages almost all the major muscle groups in your body, providing an excellent full-body workout. From your arms and shoulders to your core and legs, every stroke and kick helps to strengthen and tone your muscles.
2. Improved cardiovascular health
Swimming is a cardiovascular exercise that gets your heart pumping and improves your overall cardiovascular health. It increases your heart rate, improves blood circulation, and enhances your lung capacity, contributing to a healthy heart and reducing the risk of cardiovascular diseases.
3. Increased muscle strength and endurance
Regular swimming builds muscle strength and endurance. The resistance of the water against your body helps to strengthen your muscles, including your arms, shoulders, back, and legs. As you progress, you’ll notice increased stamina and the ability to swim for longer periods.
4. Weight management
Swimming is an effective exercise for weight management. It burns calories and helps to maintain a healthy weight. The water’s buoyancy reduces the impact on your joints, making it an ideal exercise for individuals with joint problems or those looking for a low-impact workout.
5. Joint-friendly exercise
Swimming is a low-impact exercise that puts minimal stress on your joints. Unlike high-impact activities such as running or jumping, swimming provides a gentle environment for exercise. It is particularly beneficial for individuals with arthritis, joint pain, or injuries.
Mental Health Benefits
1. Stress relief
Swimming is a fantastic stress-reliever. The rhythmic movements and the sensation of water can help calm your mind and reduce stress levels. It promotes relaxation, allowing you to unwind and escape from the pressures of daily life.
2. Improved mood and mental well-being
Regular swimming has a positive impact on your mood and mental well-being. It releases endorphins, also known as “feel-good” hormones, which can elevate your mood and create a sense of happiness and contentment.
3. Enhanced cognitive function
Swimming has been linked to improved cognitive function. The combination of aerobic exercise, increased blood flow to the brain, and the overall sensory experience of swimming can enhance your cognitive abilities, including memory, focus, and problem-solving skills.
4. Reduced risk of depression and anxiety
Swimming has been shown to reduce the risk of depression and anxiety. The combination of physical exercise, relaxation, and the release of endorphins can contribute to better mental health and a reduced likelihood of developing these conditions.
Rehabilitation and Injury Prevention
1. Low-impact exercise for rehabilitation
Swimming is often recommended as a form of exercise during rehabilitation. It provides a low-impact environment that allows for gentle movement and muscle strengthening, making it ideal for recovering from injuries or surgeries.
2. Strengthening of injured muscles
Swimming can help strengthen muscles that have been injured or weakened. The water’s resistance provides a challenging yet safe environment for muscle rehabilitation, promoting healing and recovery.
3. Improved flexibility and range of motion
The range of motion required in swimming helps improve flexibility and joint mobility. Regular swimming can help maintain and enhance your overall flexibility, reducing the risk of muscle imbalances and joint stiffness.
4. Reduced risk of certain injuries
Swimming is a non-weight-bearing exercise, which means it puts less stress on your bones and joints compared to other activities like running. This can lower the risk of certain injuries, such as stress fractures, while still providing a challenging workout.
Social Benefits
1. Opportunities for social interaction
Swimming can be a social activity that allows you to connect with others who share a similar interest. Whether you join a swimming club, take swimming lessons, or participate in group exercises in the pool, swimming offers opportunities for social interaction.
2. Building relationships and connections
Swimming provides a platform to build relationships and connections with like-minded individuals. It can be a great way to meet new people, make friends, and engage in a shared passion for swimming and overall well-being.
3. Sense of community
Swimming communities can provide a sense of belonging and support. Whether it’s cheering on fellow swimmers during competitions or participating in swimming events, the sense of community fosters a positive environment that encourages growth and motivation.
Safety Precautions and Tips
1. Learning proper swimming techniques
To fully enjoy the benefits of swimming, it is essential to learn proper swimming techniques. Taking swimming lessons from a qualified instructor can help you develop efficient strokes and improve your overall swimming skills, ensuring a safe and enjoyable experience.
2. Supervision for children and beginners
When swimming, especially for children and beginners, it is crucial to have proper supervision. Always swim in designated areas with lifeguards present, and ensure children are under constant supervision to prevent accidents and ensure their safety. Hair Care When Swimming Tips and Guide
3. Swimming in safe and designated areas
Swimming in safe and designated areas, such as pools with lifeguards or beaches with designated swimming zones, is important to ensure your safety. Avoid swimming in unfamiliar or potentially hazardous bodies of water without proper supervision or knowledge of the area.
Common Mistakes to Avoid
When incorporating weight workouts into a swimming training plan, it’s important to avoid common mistakes that can hinder progress or lead to injury. Here are a few key points to keep in mind:
- Overtraining: While weight workouts are beneficial, overtraining can be counterproductive and increase the risk of injury. Allow for adequate rest and recovery between sessions.
- Improper Technique: Using correct form and technique is crucial to maximize the benefits of weight training and reduce the risk of injury. Seek guidance from a qualified strength and conditioning coach if needed.
- Neglecting Core Exercises: Core strength is essential for swimmers. Don’t overlook exercises that target the abdominal muscles, lower back, and hips.
- Ignoring Flexibility Training: Maintain flexibility through regular stretching and mobility exercises to prevent muscle imbalances and maintain a full range of motion.
Essential Weight Exercises for Swimmers
- Squats: Squats target the quadriceps, hamstrings, and glutes, helping swimmers generate power from their lower body.
- Deadlifts: Deadlifts engage the entire posterior chain, including the glutes, hamstrings, and back muscles, promoting strength and stability.
- Lunges: Lunges work the quadriceps, hamstrings, and glutes, helping to improve leg strength and stability.
- Lat Pulldowns: Lat pulldowns strengthen the muscles in the back, particularly the latissimus dorsi, which contribute to a strong and efficient pull in the water.
- Shoulder Presses: Shoulder presses target the deltoid muscles, which are crucial for maintaining proper arm positioning during swimming strokes.
- Planks: Planks engage the core muscles, including the abs, obliques, and lower back, improving core stability and body control.
- Russian Twists: Russian twists work the oblique muscles, enhancing rotational strength and stability.
- Leg Presses: Leg presses target the quadriceps, hamstrings, and glutes, helping to develop leg strength and power.
- Dumbbell Rows: Dumbbell rows strengthen the upper back and shoulder muscles, aiding in maintaining a strong and efficient pull.
- Medicine Ball Exercises: Medicine ball exercises, such as rotational throws and overhead slams, improve core strength and power transfer between the upper and lower body.
Structuring a Weight Workout Routine for Swimmers
To maximize the benefits of weight training, swimmers should structure their workouts effectively. Here’s a sample structure for a weight workout routine:
- Warm-up: Begin with a dynamic warm-up to increase blood flow, warm up the muscles, and prepare the body for exercise. Include exercises such as arm swings, leg swings, and bodyweight squats.
- Strength Training: Perform 3-4 sets of each weight exercise, with 8-12 repetitions per set. Focus on maintaining proper form and gradually increasing the weight as strength improves.
- Core Exercises: Incorporate core exercises such as planks, Russian twists, and medicine ball exercises into the workout routine. Perform 2-3 sets of each exercise, aiming for 15-20 repetitions.
- Stretching and Cool Down: Finish the workout with static stretching exercises for the major muscle groups used during the workout. This helps improve flexibility and aids in the recovery process. Remember to cool down gradually.
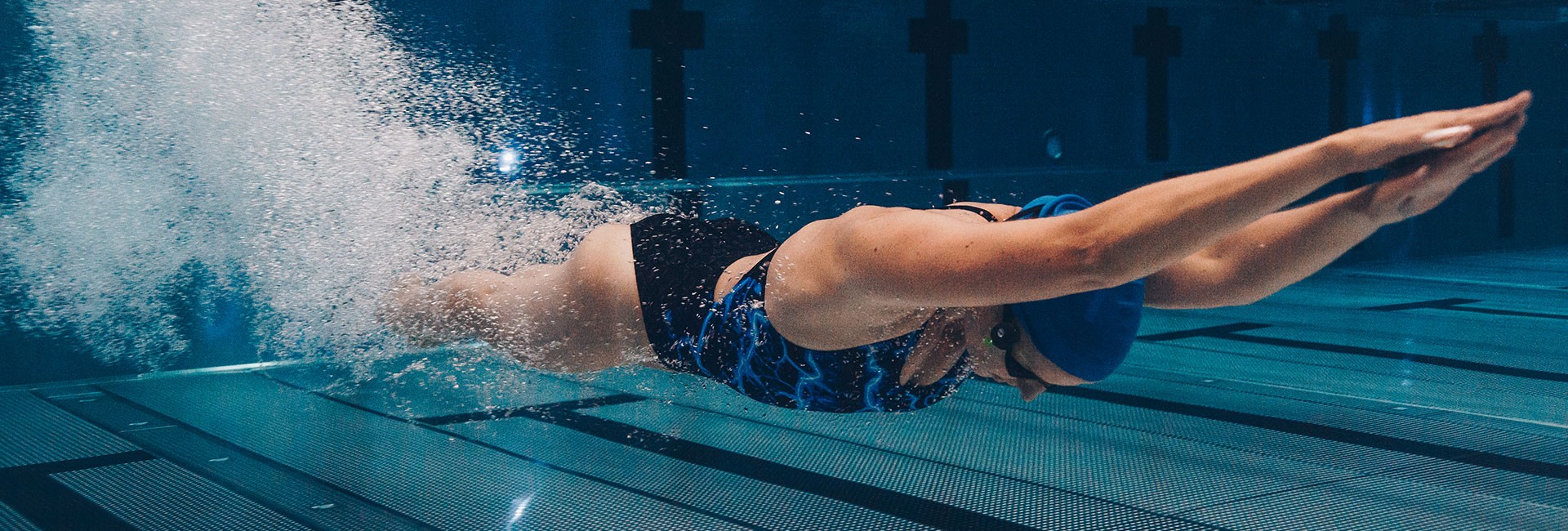
Basic Principles of Agility Training
Before diving into specific agility workouts, it’s important to understand the basic principles of agility training. Firstly, warm-up exercises should precede any agility workout to prepare the body for intense movements. Secondly, drills should focus on multi-directional movements, including forward, backward, lateral, and diagonal motions. Lastly, rest intervals between drills should be sufficient to maintain proper form and prevent fatigue-induced injuries.
Agility Drills for Swimmers
To improve agility, swimmers can incorporate various drills into their training routine. Here are four effective agility drills specifically tailored for swimmers:
1. Ladder Drills
Ladder drills involve performing a series of footwork exercises using a ladder laid flat on the ground. Swimmers can practice quick steps, lateral movements, and hopping patterns to improve foot speed, coordination, and agility.
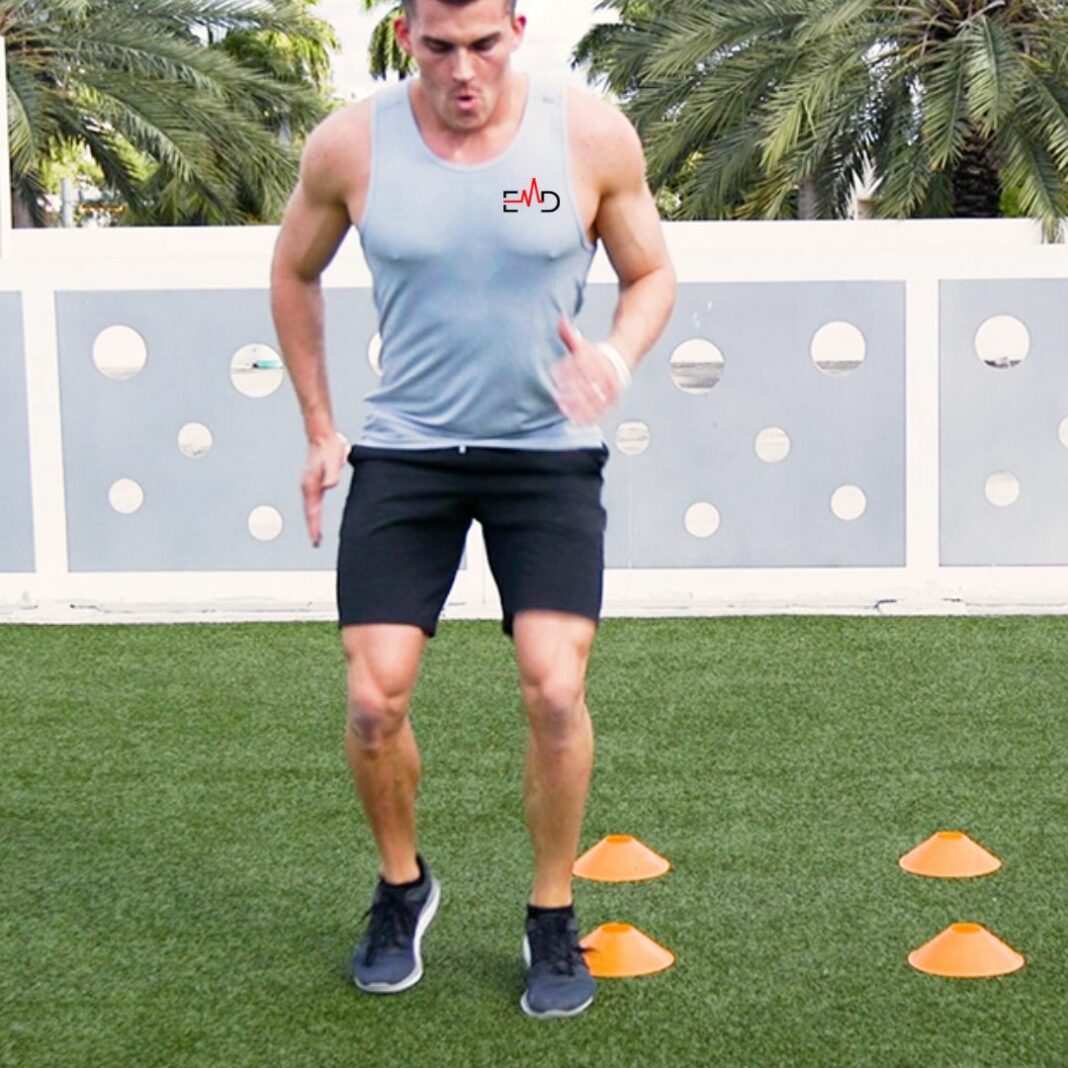
2. Cone Drills
Cone drills require swimmers to navigate through a set of cones placed at varying distances and angles. These drills improve agility, as swimmers must quickly change directions while maintaining speed and control.
3. Shuttle Runs
Shuttle runs involve sprinting back and forth between two designated points. This exercise enhances a swimmer’s acceleration, deceleration, and ability to change direction rapidly, simulating race conditions.
4. Reaction Time Exercises
Reaction time exercises focus on improving a swimmer’s responsiveness to visual or auditory cues. These exercises can involve starting from different positions in the water or reacting to commands, enhancing a swimmer’s reaction time and agility.
Incorporating Strength and Agility Training
Agility training should be complemented with strength training to maximize its benefits. Building strength in key muscle groups, such as the core, legs, and upper body, enhances a swimmer’s stability and power during agility movements.
Precautions and Safety Measures
While agility training can be highly beneficial, it’s crucial to prioritize safety. Swimmers should start with low-intensity drills and gradually increase the difficulty level to prevent injuries. Adequate warm-up, maintaining proper form, and using suitable footwear and equipment are essential safety measures to follow.
Training Frequency and Progression
The frequency and progression of agility training should be tailored to an individual swimmer’s abilities and goals. Generally, two to three sessions per week focusing on different agility drills are recommended. As swimmers progress, the complexity and intensity of drills can be gradually increased to continue challenging their agility.
Agility Equipment for Swimmers
Various equipment can be used to enhance agility training for swimmers. These include agility ladders, cones, agility hurdles, reaction balls, and resistance bands. Using such equipment adds variety to workouts and further stimulates agility development.
The Role of Agility in Injury Prevention
Agility training not only improves performance but also plays a vital role in preventing injuries. By enhancing a swimmer’s body control, coordination, and responsiveness, agility workouts help minimize the risk of falls, collisions, and overuse injuries.
Agility Workouts for Different Swimming Strokes
Agility training can be customized to benefit swimmers across different strokes. Let’s explore how agility workouts can be tailored for each stroke:
1. Freestyle
For freestyle swimmers, agility workouts can focus on quick turns, efficient starts, and maintaining a streamlined body position while executing rapid stroke movements.
2. Backstroke
Backstroke swimmers can benefit from agility drills that enhance their ability to perform quick flips and underwater turns, as well as maintain body control while swimming on their backs.
3. Breaststroke
Agility training for breaststroke swimmers can include drills that improve their ability to execute fast pullouts, efficient stroke recoveries, and powerful kick transitions.
4. Butterfly
Butterfly swimmers can enhance their agility through drills that focus on maintaining a strong body position, executing fast and efficient underwater dolphin kicks, and performing quick and precise turns.
Agility Training for Open Water Swimmers
Open water swimmers face unique challenges that require specific agility training. Exercises that simulate unpredictable conditions, such as waves or currents, can help open water swimmers improve their adaptability and responsiveness in different environments.
Incorporating Agility into Swim Practices
To make the most of agility training, coaches and swimmers can incorporate agility exercises into regular swim practices. By dedicating specific time slots for agility drills, swimmers can seamlessly integrate agility development into their overall training routine.
Nutritional Considerations for Swimmers
Optimal nutrition plays a vital role in supporting swimmers’ agility and overall performance. A well-balanced diet rich in lean proteins, whole grains, fruits, and vegetables provides the necessary nutrients for energy, muscle recovery, and overall health.
Conclusion
Incorporating gym workouts into a swimmer’s training routine can significantly enhance swimming performance. By targeting specific muscle groups, building strength and power, improving endurance, and working on agility and stability, swimmers can reach new levels of excellence in the water. Additionally, the health benefits of swimming itself make it a valuable activity for overall fitness and well-being.
FAQs – Gym Workouts for Swimmers
Q. Can gym workouts alone improve swimming performance?
While gym workouts can enhance swimming performance, they should be combined with regular swimming practice for optimal results.
Q. How often should swimmers incorporate weight workouts into their training?
It is recommended to incorporate weight workouts 2-3 times a week, with adequate rest days in between to allow for muscle recovery.
Q. Are spin workouts suitable for swimmers of all levels?
Yes, spin workouts can be adapted to different fitness levels. Beginners should start at a comfortable pace and gradually increase the intensity.
Q. Can agility workouts help with stroke efficiency?
Yes, agility workouts improve swimmers’ ability to change direction quickly, which can translate to better stroke technique and efficiency.
Q. What are some safety tips to consider when doing gym workouts for swimmers?
Always warm up before workouts, maintain proper form and technique, listen to your body, and consult a trainer or coach for guidance to minimize the risk of injuries.




