Exercise Daily – Microwaves are a part of our daily lives. We rely on them to heat food quickly and efficiently. In this guide, we’ll explore everything you need to know about microwave radiation, including what a microwave is, how a microwave oven works, the science behind microwave radiation, and the potential health risks. We’ll also share essential safety tips to ensure you use your microwave safely. So, let’s dive in and clear up any confusion once and for all!
What is Microwave Radiation?
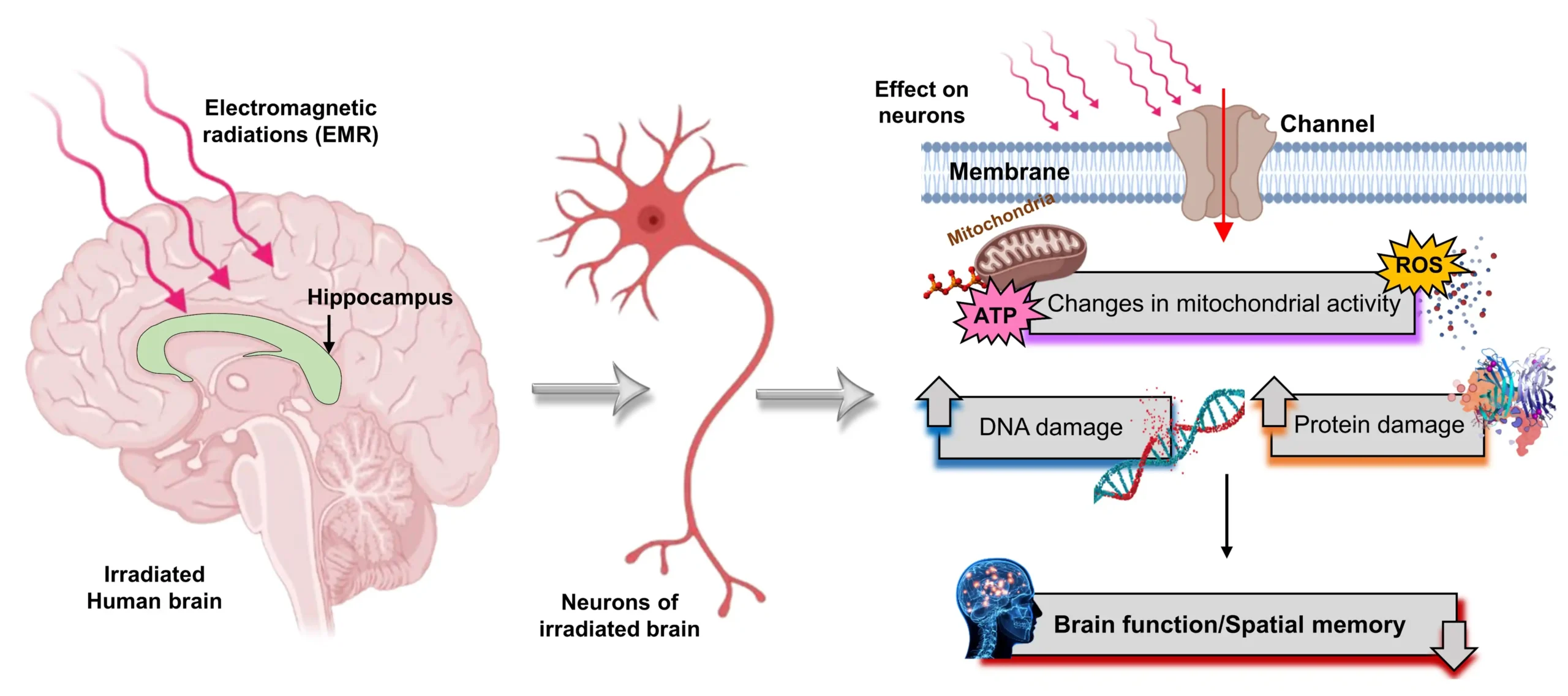
Microwave radiation is a form of electromagnetic radiation that falls within the electromagnetic spectrum. It has a wavelength ranging from one millimeter to one meter, with frequencies between 300 MHz and 300 GHz. Microwaves are a type of non-ionizing radiation, which means they do not have enough energy to remove tightly bound electrons from atoms or molecules. This makes microwaves fundamentally different from ionizing radiation, like X-rays and gamma rays, which are capable of causing cellular damage.
How Microwave Ovens Use Microwave Radiation
Microwave ovens use microwave radiation to heat food by causing water molecules in the food to vibrate. These vibrating molecules produce friction, which generates heat and warms up the food. The microwave energy used in microwave ovens typically operates within the 2.45 GHz frequency range, an ideal frequency for exciting water molecules. As a result, microwave ovens can quickly heat food and cook it evenly.

The Safety of Microwave Radiation: Non-Ionizing vs. Ionizing
One of the key distinctions to make when discussing microwave radiation is that it is non-ionizing radiation. Unlike ionizing radiation, which can cause changes at the molecular level and damage DNA, microwave radiation does not have the energy to ionize atoms or molecules. Therefore, the potential health risks of microwave radiation are less severe than those associated with ionizing radiation.
Are Microwave Ovens Safe?
Microwave ovens are generally considered safe when used correctly. The Food and Drug Administration (FDA) sets and enforces standards to ensure that microwave ovens meet safety requirements. According to the FDA, microwave ovens must be designed in such a way that radiation leakage is kept to a minimum. Microwaves produced by the oven are contained inside the appliance as long as the door is closed properly, preventing exposure to potentially harmful radiation.
Radiation Leaks and Health Risks
Although microwave ovens are generally safe, there are some concerns about potential radiation leakage. When a microwave oven is in good working condition and the door is properly sealed, radiation leakage is minimal. However, if the microwave’s door seal is damaged or the door is left open during operation, it may allow microwave radiation to leak out. In such cases, exposure to microwave radiation could be harmful.
The effects of microwave radiation exposure are still a subject of ongoing research. Some studies have suggested that long-term exposure to high levels of microwave radiation could potentially affect biological systems. However, the radiation levels emitted by microwave ovens are far lower than those that would cause harm. The FDA and other regulatory agencies have set strict limits on microwave radiation leakage to ensure that it does not exceed safe levels.
Microwave Ovens and Their Safety Standards
The FDA requires that all microwave ovens meet strict performance standards. These standards ensure that microwave ovens are designed to minimize radiation leakage and operate safely. Microwave ovens must have a label stating that they meet these standards, providing consumers with peace of mind.
In addition to meeting safety standards, microwave ovens are designed with multiple safety features, including a metal mesh in the door that helps keep radiation contained. The door’s design is also crucial in preventing exposure to microwave radiation. When the door is opened during operation, the microwave energy is immediately cut off to prevent any harm.
Potential Health Effects of Microwave Radiation
So, does microwave radiation pose any health risks? The short answer is no, not when used properly. However, it’s important to consider potential health concerns, especially if microwave radiation is not contained properly within the oven.
Tissue Heating
The primary effect of microwave radiation on the human body is heating. Prolonged exposure to high levels of microwave radiation can cause tissue to heat up, which could lead to burns or other injuries. This is why microwave ovens are designed with shielding to prevent radiation from escaping.
Eye Damage
The eye is particularly sensitive to microwave radiation. Prolonged exposure to microwave radiation can cause damage to the eye’s lens and retina, leading to cataracts. However, such exposure is unlikely unless the microwave oven is damaged or malfunctioning.
Potential Cancer Risk
There is no direct evidence linking microwave radiation from microwave ovens to cancer. However, microwave radiation can cause changes in cells and tissues if exposure is high enough. It’s important to note that the levels of radiation emitted by microwave ovens are far below those that would pose a cancer risk.
Electromagnetic Hypersensitivity
Some individuals report symptoms such as headaches, fatigue, and dizziness when exposed to microwave radiation or other types of electromagnetic radiation. This condition, known as electromagnetic hypersensitivity, is controversial, as no scientific studies have conclusively proven that microwave radiation causes these symptoms.
How to Use Microwave Ovens Safely
While the health risks of microwave radiation are minimal when the microwave is used correctly, it’s still important to follow a few safety guidelines:
- Follow the Manufacturer’s Instructions: Always follow the manufacturer’s instructions for use, including the proper placement of food and the use of safe containers.
- Do Not Use a Damaged Microwave Oven: If you notice any damage to the door, seal, or other parts of the microwave oven, stop using it until it is repaired. A damaged microwave can cause radiation leakage.
- Keep the Microwave Clean: Regularly clean the interior of the microwave to prevent food spills and stains from damaging the appliance.
- Ensure the Door is Properly Sealed: Before using the microwave, make sure the door is completely closed and sealed to prevent microwave radiation from leaking out.
- Limit Exposure: If you’re concerned about exposure to microwave radiation, stand a few feet away from the microwave while it’s in use.
Further Insights into Microwave Radiation and Its Safety
The mechanism through which microwave radiation heats food is fascinating and unique. Microwave ovens rely on microwave energy, a type of electromagnetic radiation, to cook or heat food. Microwaves are absorbed by water molecules in the food, causing these molecules to vibrate rapidly. As these molecules vibrate, they create friction, which generates heat.
The Role of Water Molecules in Microwave Heating
Water plays a crucial role in the heating process in microwave ovens. When microwave radiation is used, the energy is absorbed by water molecules in the food. The energy causes the water molecules to move, or vibrate, at a high speed, generating heat. The heat is then transferred to the surrounding food, ensuring it is heated evenly. This is why foods that have a higher water content—such as soups, vegetables, and meats—tend to cook more efficiently in microwave ovens.
Understanding the Microwave Oven Design
Microwave ovens are meticulously designed to ensure safety during their operation. Every microwave oven is equipped with shielding mechanisms to contain microwave radiation within the appliance. These shields include the metal casing and a metal mesh on the microwave door. The metal mesh is designed to allow you to see inside the microwave oven while preventing any microwave radiation from escaping. The design ensures that microwave radiation is confined to the interior of the oven, where it is used to heat the food.
Regulation and Safety Standards for Microwave Ovens
The FDA regulates microwave ovens to ensure they meet strict safety standards. These standards are based on scientific research and extensive testing to ensure that microwave ovens are safe for everyday use. For example, the FDA has set limits on the amount of radiation leakage that is acceptable. Microwave ovens must meet these limits to ensure that the radiation emitted during operation is not harmful to users.
Common Myths About Microwave Radiation
There are several common myths surrounding microwave radiation, and it’s important to separate fact from fiction to use microwave ovens safely and confidently. Let’s debunk the top three myths that often cause confusion and concern.
Myth 1: Microwaves cause cancer.
This is one of the most widely spread myths. The idea that microwave radiation can cause cancer comes from confusion between non-ionizing radiation and ionizing radiation. Microwaves, like the ones used in microwave ovens, are non-ionizing radiation, which means they don’t have enough energy to strip electrons from atoms or alter DNA—two factors that can lead to cancer.
In contrast, ionizing radiation (such as X-rays or gamma rays) can cause these changes, which is why it’s considered harmful. Microwave ovens are designed with safety features that contain radiation within the unit, ensuring that there’s no direct exposure to harmful radiation. To date, no credible studies have shown any direct link between the use of microwave ovens and cancer.
Myth 2: Microwaved food loses nutrients.
Another common myth is that microwaving food causes it to lose more nutrients compared to other cooking methods. However, this is not true. The truth is that microwave cooking is one of the best methods for preserving nutrients in food. The reason is that microwaves cook food quickly and require little to no water. Which helps preserve water-soluble nutrients, like vitamins B and C, that are often lost during boiling or other prolonged cooking methods.
In fact, microwave cooking can help retain more nutrients compared to traditional cooking methods that expose food to heat for longer periods. Nutrient loss is minimal and comparable to any other cooking method.
Myth 3: Microwaves leak dangerous radiation.
The myth that microwaves leak dangerous radiation is another misconception. Modern microwave ovens are equipped with multiple safety mechanisms to prevent radiation leakage. The microwave radiation produced inside the oven is contained by a metal mesh in the door and the oven’s seals, which prevent any radiation from escaping.
In fact, microwave ovens must meet strict safety standards set by authorities like the FDA to ensure that radiation leakage is virtually nonexistent. Even if a microwave door becomes damaged, it’s unlikely to leak dangerous levels of radiation. To be safe, always inspect your microwave for any visible damage and follow the manufacturer’s instructions.
Conclusion
Microwave radiation is generally safe when used correctly. Microwave ovens are designed to minimize radiation leakage and are held to strict safety standards by the FDA. While there are some potential health risks associated with microwave radiation. Such as tissue heating and eye damage, these risks are minimal when the microwave is used properly. By following safety precautions and using microwave ovens according to the manufacturer’s instructions, you can enjoy their convenience without worrying about potential health hazards.
FAQs – Microwave Radiation: Potential Health Risks and Essential Safety Tips
Q: Can microwave radiation cause cancer?
A: No, there is no direct evidence linking microwave radiation from microwave ovens to cancer. The radiation emitted by microwaves is not ionizing and does not have enough energy to damage DNA.
Q: Is it safe to stand near a microwave oven while it’s on?
A: Yes, it is generally safe to stand near a microwave oven while it is operating, as long as the door is properly sealed. Radiation leakage is minimal in properly functioning microwave ovens.
Q: Can microwave radiation affect my eyes?
A: Prolonged exposure to high levels of microwave radiation can cause eye damage. However, such exposure is unlikely unless the microwave is damaged or malfunctioning.
Q: What should I do if my microwave oven is damaged?
A: If your microwave oven is damaged, especially the door seal, it’s best to stop using it until it is repaired. A damaged microwave can cause radiation leakage.
Q: How can I reduce my exposure to microwave radiation?
A: To reduce your exposure, stand a few feet away from the microwave while it’s in use and ensure that the door is properly closed. Always follow the manufacturer’s instructions for safe use.




