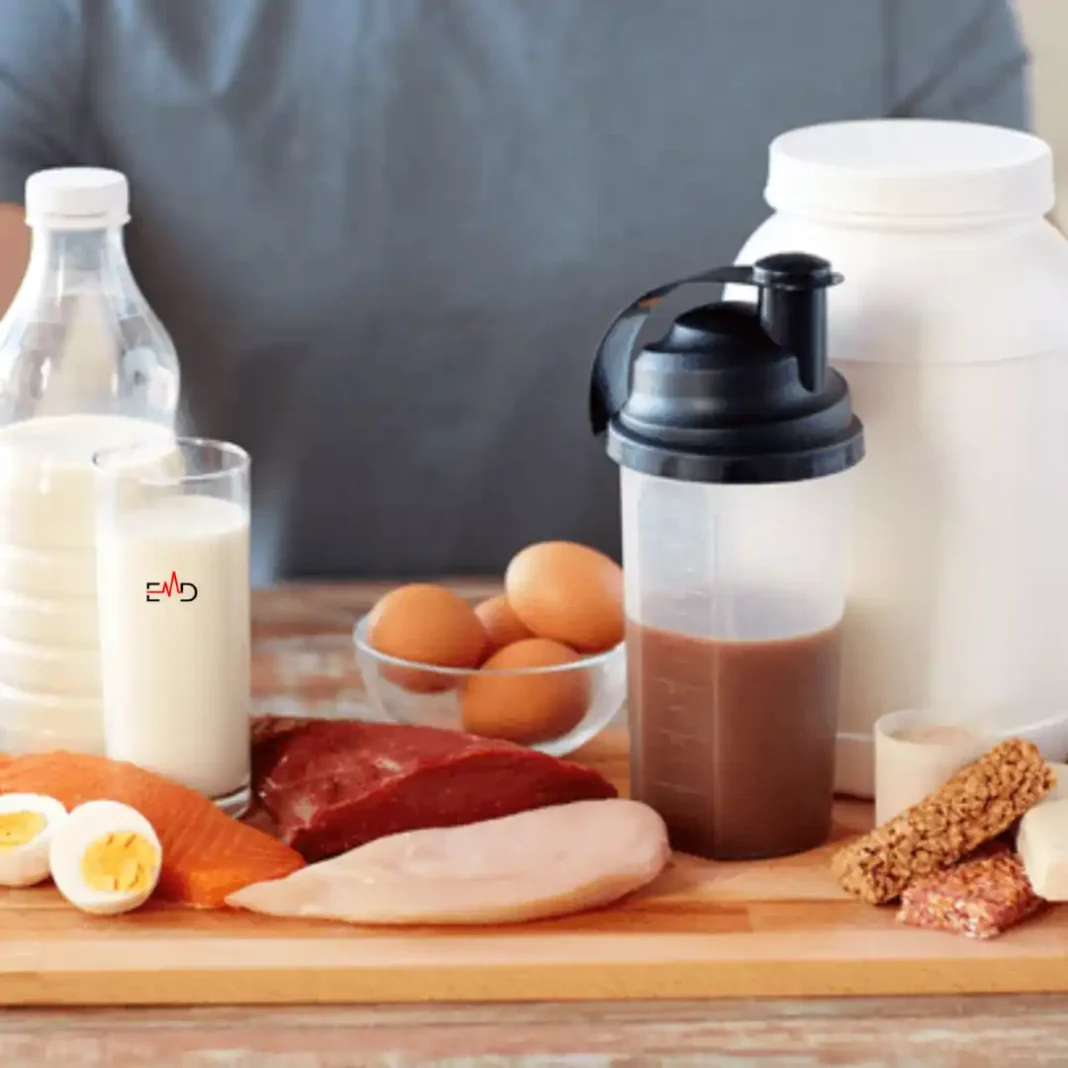
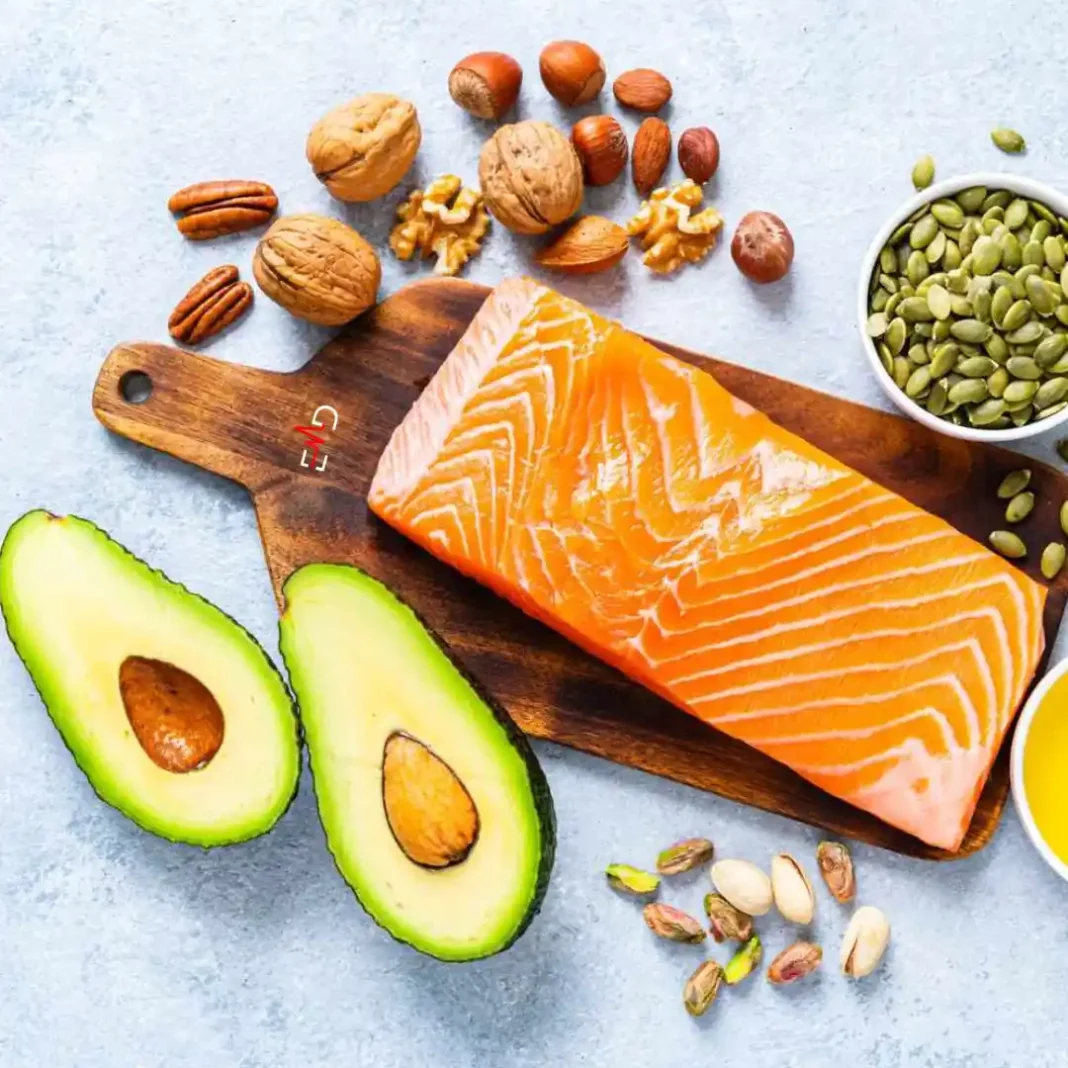
Exercise Daily – In sports medicine and the broader field of exercise science, dietary supplements have become a key component of performance strategies, especially for elite athletes and high-intensity exercise. As highlighted by research in the Journal of the International Society of Sports Nutrition and the British Journal of Sports Medicine, supplements are often used to bridge nutritional gaps, improve exercise capacity, and enhance recovery. Proper supplementation can optimize performance during endurance exercise, track and field events, or high-intensity workouts for professional athletes and trained individuals.
Popular sports supplements, including protein powders, creatine, and sports drinks, are frequently recommended by experts from institutions such as the American College of Sports Medicine and the Australian Institute of Sport. However, the prevalence of dietary supplement use also necessitates a critical evaluation of their safety and health effects, as not all products on the market deliver the claimed performance benefits.
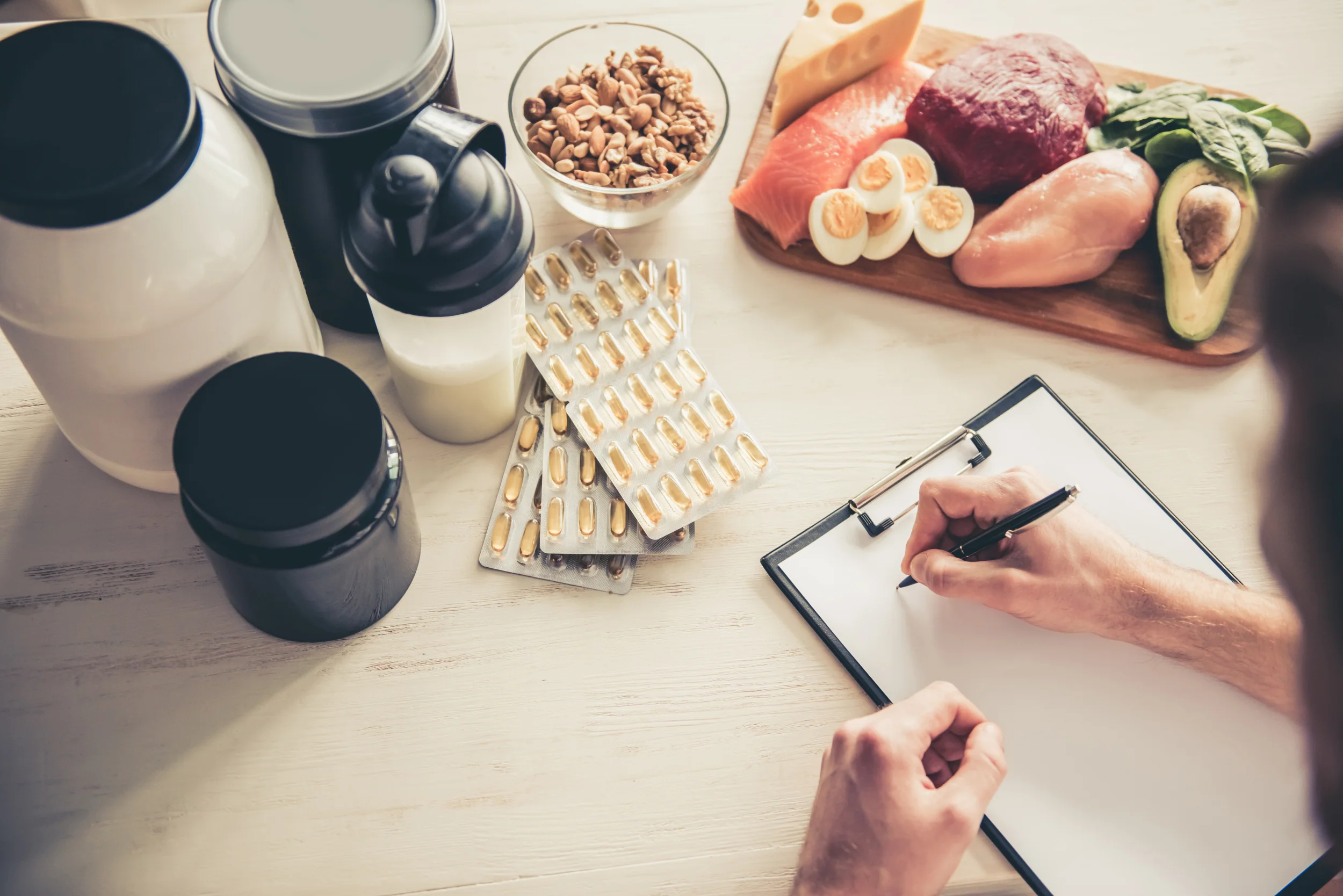

Importance of Sports Nutrition
Sports nutrition encompasses studying and practicing how diet and supplementation affect athletic performance and overall health. Proper nutrition ensures that athletes have the energy to perform at their best, the nutrients to recover effectively, and the ability to sustain their training regimens without succumbing to fatigue or injury.
- Energy Supply: Carbohydrates, proteins, and fats are the primary macronutrients that provide the energy required for training and competition. Carbohydrates, in particular, are the main fuel source during high-intensity activities.
- Muscle Repair and Growth: Proteins are essential for repairing muscle tissues damaged during intense workouts. Adequate protein intake supports muscle growth and recovery, enabling athletes to train harder and more frequently.
- Endurance and Stamina: Proper nutrition helps in maintaining endurance levels. Electrolytes and carbohydrates significantly sustain prolonged physical activities by preventing dehydration and providing continuous energy.
- Overall Health: Vitamins and minerals support various bodily functions, including immune response, bone health, and metabolic processes. Maintaining overall health ensures that athletes can train consistently without being sidelined by illnesses or deficiencies.
The Evolution of Sports Nutrition
Over the years, the field of sports nutrition has evolved significantly. Early athletes relied primarily on whole foods to meet their nutritional needs. However, as the understanding of nutritional science deepened, the integration of dietary supplements became more prevalent. The modern approach to sports nutrition emphasizes a combination of balanced diets and strategic supplementation to achieve optimal performance.
The Rise of Dietary Supplements in Sports
The use of dietary supplements among athletes has witnessed a remarkable increase over the past few decades. Several factors contribute to this surge:
- Increased Awareness: Athletes are more informed about the benefits of supplements and how they can enhance performance and recovery.
- Marketing and Availability: The supplement industry has grown exponentially, with a wide range of products available in stores and online, making them easily accessible to athletes.
- Scientific Advancements: Ongoing research has highlighted the potential benefits of various supplements, encouraging their adoption in athletic circles.
- Competitive Edge: Even marginal gains can significantly affect highly competitive sports. Supplements are often viewed as a means to gain that extra advantage.
Are Supplements Necessary?
While the popularity of supplements is undeniable, their necessity is a subject of debate. Ideally, athletes should aim to meet their nutritional needs through a balanced diet rich in whole foods. However, factors such as intense training schedules, increased nutritional requirements, and dietary restrictions can challenge achieving optimal nutrition solely through diet. In such cases, supplements can play a supportive role.
It’s essential to approach supplementation with a clear understanding of individual needs, the specific benefits of each supplement, and potential risks. Not all supplements are created equal, and their efficacy can vary based on quality, dosage, and individual response.
Core Concepts
Dietary supplements are products designed to augment the diet by providing additional nutrients that may be lacking. They come in various forms, including pills, capsules, powders, and liquids. The primary categories of dietary supplements include:
- Vitamins: Organic compounds essential for normal growth and nutrition, required in small quantities in the diet.
- Minerals: Inorganic elements that play critical roles in various bodily functions, including bone formation, nerve function, and muscle contraction.
- Amino Acids: The building blocks of proteins, crucial for muscle repair and growth.
- Herbal Extracts: Plant-based compounds believed to have specific health benefits, such as boosting energy or enhancing recovery.
- Other Specialized Supplements: Including fatty acids, probiotics, and antioxidants that support overall health and specific athletic needs.
Sports Nutrition: A Foundation for Athletes
Before incorporating supplements into their regimen, athletes should prioritize a well-rounded, balanced diet. A solid nutritional foundation includes:
- Proteins: Necessary for muscle repair and growth. Sources include lean meats, dairy products, legumes, and plant-based proteins.
- Carbohydrates: The primary energy source for high-intensity activities. Whole grains, fruits, and vegetables are excellent sources.
- Healthy Fats: Essential for energy, hormone production, and cell function. Sources include avocados, nuts, seeds, and olive oil.
- Vitamins and Minerals: Crucial for various bodily functions, including immune support and bone health. A diverse diet of fruits, vegetables, and whole foods typically provides adequate amounts.
Supplements should be viewed as an adjunct to, not a replacement for, a nutritious diet. They are most effective when used to address specific deficiencies or to support particular training demands.
Types of Supplements
Dietary supplements come in various forms, each serving a distinct purpose in sports nutrition. Understanding the different types can help athletes choose the most appropriate supplements.
Protein Supplements: A Must for Muscle Recovery
Types of Protein Supplements
- Whey Protein: Derived from milk, whey is quickly absorbed by the body, making it ideal for post-workout recovery. It contains all essential amino acids, making it a complete protein source.
- Casein Protein: Also derived from milk, casein is absorbed more slowly, providing a steady release of amino acids over several hours. It’s often consumed before bedtime to support overnight muscle repair.
- Plant-Based Proteins: Options like pea, soy, and hemp protein cater to vegetarians, vegans, and those with lactose intolerance. While some plant proteins may lack certain amino acids, blends can provide a complete profile.
Benefits for Athletes
- Muscle Repair: Protein supplements supply amino acids to repair muscle tissues damaged during intense workouts.
- Muscle Growth: Regular protein intake supports hypertrophy, enabling athletes to increase muscle mass and strength.
- Convenience: Protein powders offer a quick and easy way to meet daily protein requirements, especially when whole food sources are insufficient or impractical.

Vitamin and Mineral Supplements: Essential Micronutrients
Vitamins and minerals are pivotal in energy production, bone health, immune function, and oxygen transport. Athletes, due to their heightened physical demands, often have increased needs for certain micronutrients.
Common Supplements
- Vitamin D: Essential for bone health and immune function. Many athletes, especially those training indoors or in regions with limited sunlight, may be deficient.
- Calcium: Crucial for bone strength and muscle function. Adequate calcium intake helps prevent stress fractures and supports overall skeletal health.
- Iron: Vital for oxygen transport in the blood. Female athletes, in particular, are at risk of iron deficiency, which can impair performance and endurance.
- Magnesium: Involved in muscle contraction and energy production. It also helps prevent cramps and supports recovery.
Benefits for Athletes
- Enhanced Performance: Proper micronutrient status ensures optimal metabolic function and energy production.
- Injury Prevention: Strong bones and muscles reduce the risk of fractures and strains.
- Immune Support: Adequate vitamins and minerals bolster the immune system, helping athletes stay healthy during intense training.
Athletes and coaches should adopt a science-backed approach to supplementation, integrating guidance from the Journal of Sports Medicine and other reputable sources. The use of nutritional supplements must align with the specific demands of exercise training and the athlete’s individual needs. Supplements designed to enhance exercise performance, such as beta-alanine and branched-chain amino acids, can improve endurance exercise and recovery. Still, improper use or reliance on unregulated products may impair exercise performance or pose serious health risks.
Professional guidance, such as consulting the Academy of Nutrition and Dietetics or talking to a healthcare provider, is essential for ensuring supplements improve the performance of athletes safely and effectively. Ultimately, the intersection of sports nutrition and supplementation requires informed choices to achieve both health and athletic goals.
Creatine Supplements: Power Boosters
Creatine is a naturally occurring compound found in small amounts in certain foods and synthesized by the body. It is critical in energy production, particularly during high-intensity, short-duration activities.
Benefits for Athletes
- Increased Strength: Creatine enhances the body’s ability to produce ATP, the primary energy currency, improving strength and power output.
- Enhanced Performance: It allows athletes to perform more repetitions or sustain high-intensity efforts for longer periods.
- Muscle Growth: Creatine supplementation can increase muscle mass through improved performance and cell volumization.
Usage and Dosage
A typical creatine regimen involves a loading phase of 20 grams daily for 5-7 days, followed by a maintenance dose of 3-5 grams daily. However, some athletes opt for a consistent daily dose without a loading phase to avoid potential gastrointestinal discomfort.
Other Notable Supplements
While protein, vitamins, minerals, and creatine are among the most popular, several other supplements are commonly used in sports nutrition:
- Branched-Chain Amino Acids (BCAAs): Promote muscle protein synthesis and reduce muscle soreness.
- Electrolytes: Help maintain fluid balance and prevent cramps during prolonged exercise.
- Omega-3 Fatty Acids: Support cardiovascular health and reduce inflammation.
- Pre-Workout Blends: Contains caffeine, beta-alanine, and nitric oxide boosters to enhance energy and focus.
Supplement Use
Athletes incorporate supplements into their diets for various reasons:
- Recovery: Supplements like protein powders and BCAAs aid muscle repair and reduce recovery time between workouts.
- Performance Enhancement: Creatine and pre-workout supplements can improve strength, endurance, and overall performance during training and competitions.
- Nutritional Gaps: Even with a balanced diet, certain nutrients may be lacking. Supplements ensure that athletes meet their daily nutritional requirements.
- Convenience: Supplements offer a quick and easy way to consume essential nutrients, especially when whole food options are impractical due to time constraints or training schedules.
Popular Sports Nutrition Supplements
- Protein Powders: As discussed, they are fundamental for muscle repair and growth.
- Branched-Chain Amino Acids (BCAAs): Comprising leucine, isoleucine, and valine, BCAAs support muscle protein synthesis and reduce muscle fatigue.
- Creatine: Enhances strength and power output, beneficial for high-intensity sports.
- Pre-Workout Blends: Formulated to increase energy, focus, and endurance during workouts. Common ingredients include caffeine, beta-alanine, and nitric oxide precursors.
- Electrolytes: Maintain hydration and prevent cramps during prolonged physical activities.
Supplement Claims and Labels
Navigating supplement labels can be challenging due to the myriad of claims and proprietary blends. Here are key considerations:
- Ingredient Transparency: Look for products that clearly list all ingredients and their dosages. Avoid proprietary blends that obscure the amounts of each ingredient.
- Third-Party Testing: Certifications from organizations like NSF International or Informed-Sport indicate that the product has been tested for quality and banned substances.
- Avoid Over-Promises: Be wary of supplements that claim to deliver miraculous results. Effective supplementation requires consistency and realistic expectations.
- Check for Banned Substances: Athletes subject to doping regulations should ensure their supplements are free from prohibited substances to avoid disqualification and health risks.

Effects on Performance
When used appropriately, supplements can significantly impact various aspects of athletic performance:
- Endurance: Supplements like electrolytes and carbohydrates sustain energy levels and prevent fatigue during prolonged activities.
- Strength and Power: Creatine and protein supplements enhance muscle strength and power output, allowing athletes to train harder and perform better.
- Recovery: Protein, BCAAs, and certain vitamins and minerals expedite muscle repair and reduce soreness, enabling quicker turnaround between training sessions.
- Mental Focus: Ingredients in pre-workout supplements, such as caffeine and amino acids, improve concentration and reduce perceived exertion during workouts.
Supplements for Endurance and Strength Athletes
Different types of athletes may benefit from specific supplements tailored to their sport’s demands:
Endurance Athletes
- Carbohydrate Supplements: Provide a readily available energy source during long-duration events.
- Electrolytes: Prevent dehydration and maintain muscle function by replenishing lost minerals like sodium, potassium, and magnesium.
- Beta-Alanine: Delays muscle fatigue by buffering acid buildup in muscles during high-intensity efforts.
- Caffeine: Enhances alertness and reduces the perception of effort, improving endurance performance.
Strength Athletes
- Protein Supplements: Support muscle growth and repair, essential for strength gains.
- Creatine: Boosts ATP production, increasing strength and power during explosive movements.
- Beta-Alanine: Enhances muscular endurance, allowing for more repetitions and heavier lifts.
- Branched-Chain Amino Acids (BCAAs): Reduce muscle soreness and support muscle protein synthesis.
Health and Safety
While supplements can offer benefits, they also carry potential health risks:
- Unregulated Ingredients: Some supplements contain substances not listed on the label, which can cause adverse effects or lead to unintended doping violations.
- Overconsumption: Excessive intake of certain vitamins and minerals can lead to toxicity and health complications. For example, too much vitamin D can cause hypercalcemia, and excessive iron can result in organ damage.
- Interactions with Medications: Supplements may interact with prescription or over-the-counter medications, altering their effectiveness or causing harmful side effects.
- Contamination: Poor manufacturing practices can result in contamination with harmful substances, such as heavy metals or banned performance-enhancing drugs.
The Role of Regulation in Supplement Safety
Regulation of dietary supplements varies globally, affecting their safety and quality:
- United States: The Food and Drug Administration (FDA) oversees dietary supplements under the Dietary Supplement Health and Education Act (DSHEA). However, the FDA does not approve supplements, and manufacturers are responsible for ensuring safety.
- European Union: The European Food Safety Authority (EFSA) regulates supplements, requiring safety assessments and labeling standards.
- Other Regions: Countries like Australia and Canada have regulatory frameworks, which may include mandatory testing and certification for supplement products.
Choosing Safe Supplements
To minimize health risks, athletes should:
- Opt for Reputable Brands: Choose supplements from established brands with a quality and transparency track record.
- Seek Third-Party Certification: Look for certifications from organizations like NSF International, Informed-Sport, or USP, which verify the product’s quality and purity.
- Consult Healthcare Professionals: Before starting any supplement, consult with a healthcare provider or a sports nutritionist to ensure it aligns with individual health needs and athletic goals.
- Stay Informed: Keep abreast of the latest research and regulatory updates regarding supplement safety and efficacy.

Conclusion
Diet and supplementation are intertwined elements of sports nutrition, each playing a distinct role in supporting athletic performance and health. While a balanced diet rich in whole foods forms the foundation of optimal nutrition, supplements can provide targeted support to enhance performance, aid recovery, and fill nutritional gaps. However, supplementation should be cautiously approached, emphasizing quality, evidence-based choices, and professional guidance. By prioritizing whole foods and using supplements judiciously, athletes can achieve their performance goals while maintaining overall well-being.
FAQs – Understanding the Role of Supplements in Sports Nutrition
Q: Are dietary supplements safe for athletes?
A: Dietary supplements can be safe for athletes if sourced from reputable brands that undergo third-party testing for quality and purity. It’s crucial to check for certifications from trusted organizations and consult a healthcare professional to ensure the supplements align with individual health needs and do not contain banned substances.
Q: What are the best supplements for beginners?
A: Beginners should start with foundational supplements such as protein powders to support muscle recovery and growth and multivitamins to ensure adequate micronutrient intake. It’s advisable to avoid complex pre-workout blends until understanding how one’s body responds to simpler supplements.
Q: Can supplements improve performance instantly?
A: Supplements do not provide instant performance enhancements. While certain supplements like caffeine can offer immediate effects, most supplements improve performance over time through consistent use and proper training and nutrition.
Q: Do young athletes need supplements?
A: Most young athletes can meet their nutritional needs through a balanced diet. Supplements should only be considered if there is a proven deficiency or specific nutritional need, and they should be used under the guidance of a healthcare professional or a qualified nutritionist.
Q: What are the risks of taking unregulated supplements?
A: Unregulated supplements can pose significant risks, including the presence of harmful or banned substances that can lead to health issues or failed doping tests. Choosing supplements tested for purity and quality by reputable third-party organizations is essential.




